Icequakes (Bloop)
The broad spectrum sounds recorded in the summer of 1997 are consistent with icequakes generated by large icebergs as they crack and fracture. NOAA hydrophones deployed in the Scotia Sea detected numerous icequakes with spectrograms very similar to “Bloop”. The icequakes were used to acoustically track iceberg A53a as it disintegrated near South Georgia Island in early 2008. Icequakes are of sufficient amplitude to be detected on multiple sensors at a range of over 5000 km. Based on the arrival azimuth, the iceberg(s) generating “Bloop” most likely were between Bransfield Straits and the Ross Sea, or possibly at Cape Adare, a well know source of cryogenic signals.
Click on spectrograms for full-sized image.
| Original icequake (bloop) sound: Recorded signal sped up 16 times. | 162K wav file | 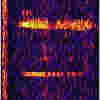 |
| Calving: Spectrogram of an iceberg calving (large section of iceberg breaking off) while adrift. The calving signal is short duration, broad band from 1-440 Hz generated by ice cracking and crack propagation. Audio sped up 3X normal. | 4.3MB wav file | 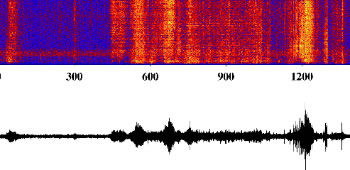 |
| Iceberg Harmonic Tremor: Generated by iceberg in contact with the seafloor or other iceberg. This spectrogram has a fundamental frequency of 40 Hz, with a 40 Hz overtone spacing. Multiple overtones are visible in the spectrogram. Audio sped up 3X normal. | 271K wav file | 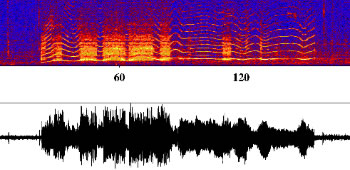 |
