Editor's Highlight: Robot Measures Air-Sea CO2 Exchange in Southern Ocean
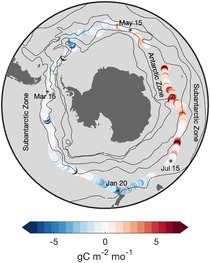
The Southern Ocean plays an outsized role in the uptake of heat and carbon, however, it is an incredibly challenging environment to make observations due to its size, remoteness, and harsh conditions. In 2019, PMEL's award-winning use of new Uncrewed Surface Vehicle technology allowed for direct measurements of CO2 exchange between the ocean and atmosphere, even during severe storms during winter months. The new observations suggest that interannual variability and potential bias in different methods to estimating CO2 flux are likely major drivers of discrepencies between CO2 uptake results from past studies. The large varibility in both time and space suggest that expansion of an observing network made up of ships, USVs, and other autonomous devices is necessary to reduce uncertainty in the Southern Ocean's role in the global carbon system.
Read more about this research by accessing the the paper in Geophysical Research Letters, the Eos Editor's Highlight, or the NOAA Research news story.